Vadim Chugunov, Chief support manager at ACBaltica
Every SAP system goes through its own lifecycle. It must be designed, built, tested, launched, supported, and improved. And something has to keep all of this under control. That “something” is Application Lifecycle Management (ALM): a product that keeps your SAP landscape healthy, your project implementation organized, and your systems working as they should. Think of ALM as the central hub that knows everything happening across your SAP environment.For years, this role belonged to SAP Solution Manager (SolMan) — a solid but heavily on-premise product launched in the mid-2000s. It worked well in its time, but the SAP world has changed. Cloud solutions are now the standard, and SolMan simply couldn't keep up.
That’s precisely why SAP Cloud ALM was created. It’s fast, cloud-native, and fully aligned with SAP’s modern strategy. It's a new way to manage the entire lifecycle of your SAP solutions.
This guide explains how SAP Cloud ALM works, how it supports each stage of the SAP solutions lifecycle, and why it is becoming the primary ALM tool for modern SAP customers.
What Is SAP Cloud ALM?
SAP Cloud ALM is a cloud-based SaaS platform that helps companies manage the full lifecycle of their SAP solutions. The platform is designed primarily for cloud-centric and hybrid SAP landscapes. It can connect to certain on-premise systems, although its capabilities for traditional on-premise environments are limited.
Cloud ALM works on SAP Business Technology Platform (SAP BTP) and is automatically included in SAP Enterprise Support as well as all SAP cloud subscriptions. SAP Cloud ALM tenant includes:
-
24 GB of SAP HANA memory
-
24 GB of outbound API traffic each month
For most companies, this is more than enough to run projects, monitor systems, and manage daily operations. If the workload increases, such as with more monitoring data, integrations, or API usage, the customer can simply purchase additional capacity.
Cloud ALM brings all landscape information into one place. It provides visibility into systems, operations, projects, and monitoring without the need to install any tools separately.
SAP Cloud ALM supports all key points of SAP solution lifecycle: implementation, operations, and service.
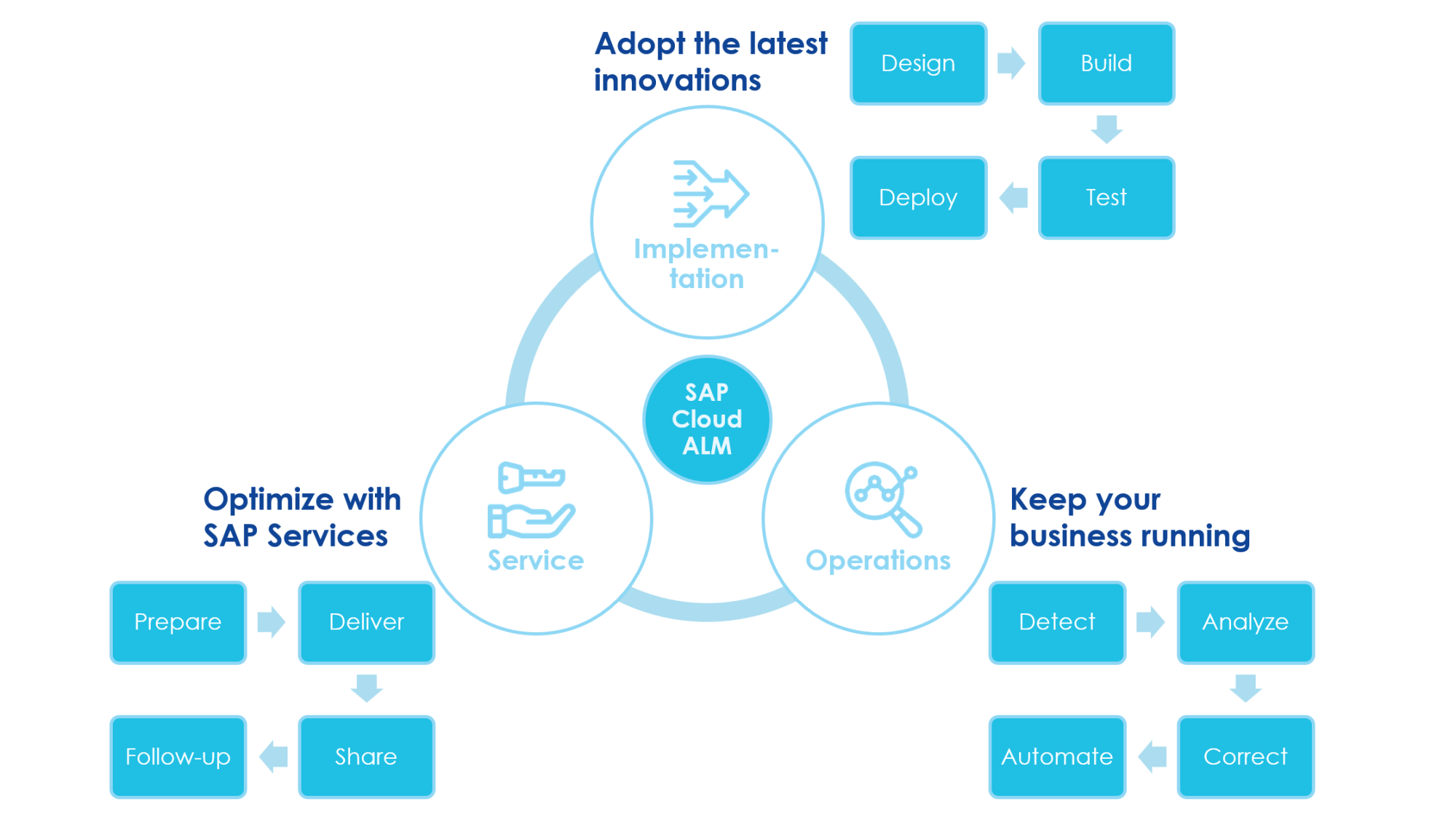
SAP ALM & SAP Activate
SAP Cloud ALM can work hand in hand with the SAP Activate methodology, which is SAP’s standard approach for implementing cloud and hybrid solutions. SAP Activate provides ready-made implementation templates and SAP Best Practices, helping project teams follow a proven structured method from the very beginning.
Creating a project in SAP Cloud ALM allows you to select an Activate roadmap. Once selected, Cloud ALM will automatically load Activate aligned content according to the selected best practice, including predefined phases, deliverables, tasks, best-practice process models, and accelerators. This provides teams with an instant project structure, eliminating the need for manual setup. Tasks delivered through best practice are organized by role, so each team member sees activities relevant to their responsibilities.
With the methodology in place, we can look at how SAP Cloud ALM actually supports project work during the implementation lifecycle.
SAP Cloud ALM for implementation
SAP Cloud ALM offers a clear, structured approach to managing the implementation of SAP solutions. It ensures the system is delivered in a controlled, transparent way, supporting teams through all key project management phases: design, build, test, and deploy.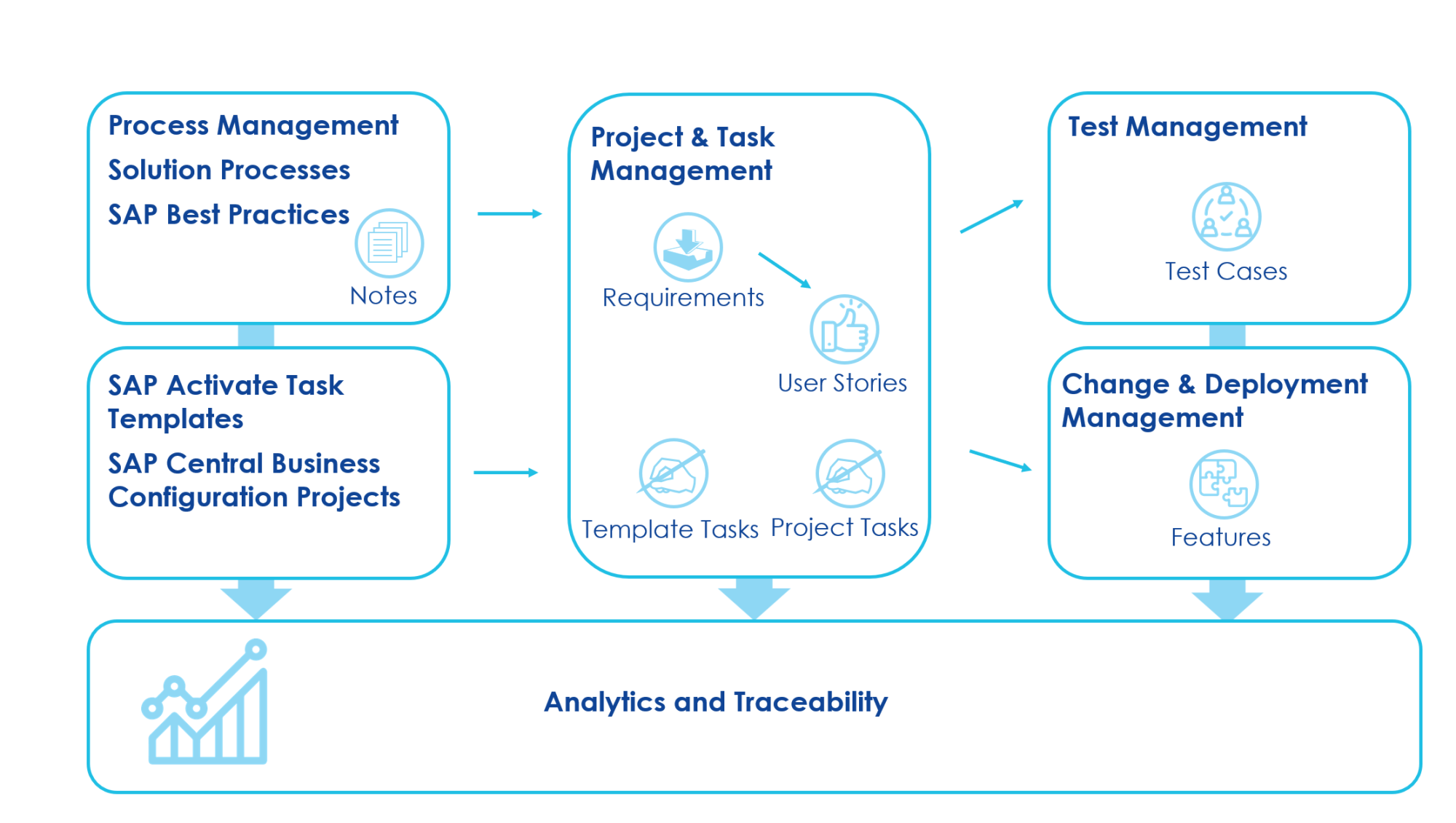
Design phase
The design phase marks the beginning of any SAP implementation. In SAP Cloud ALM, this stage involves understanding business requirements, mapping processes, and preparing the project for execution.
During this phase, teams should:
-
Invite users and assign them to SAP Activate Roles and Teams.
-
Structure project timelines with Phases, Sprints, and Milestones.
-
Select SAP Activate Methodology Roadmap per SAP Product
-
Activate SAP Best Practice Content and Intelligent Enterprise Scenarios.
-
Confirm how standard SAP processes fit the customer’s needs.
-
Run Fit-to-Standard workshops with the customer.
-
Document decisions, gaps, and requirements.
-
Convert all results into structured SAP Cloud ALM artifacts (requirement, user story, features).
-
Create own Processes with integrated process modeling capabilities.
Cloud ALM provides ready-to-use process models and guidance, which helps speed up the design work and ensures consistency with SAP best practices.
Build phase
After the design phase, the project moves into the build phase, during which configuration and development occur. During this stage, SAP Cloud ALM transforms the requirements defined in the design phase into deliverable features. Meanwhile, the project team manages tasks, sprints, and releases. This establishes a clear connection between the customer's needs and the work the team must complete to fulfill them.
In Cloud ALM, the Build phase is supported through:
-
Agile methodology: Sprints, User Stories, and Story Points
-
SAP Activate roadmaps
-
Gantt-Chart View for visualization of the project timeline and dependencies
-
Break down Requirements in User Stories and Tasks
-
Work distribution using subtasks
-
Integrated analytics
Cloud ALM makes it easy to manage workloads, follow deadlines, and maintain control over all changes being made to the system.
Test phase
Once configuration is ready, the next step is testing. SAP Cloud ALM provides tools to plan, organize, and execute tests efficiently.
Cloud ALM supports automated testing through integration with external tools such as the S/4HANA Test Automation Tool, Tricentis, and any other automation solution via Open API. This way, you can combine manual and automated tests, with the automated tests being part of the regression testing.
During this phase, teams can:
-
Create test cases based on requirements.
-
Group test cases into test plans organizing related tests into a single, manageable collection.
-
Assign tests to testers.
-
Track execution progress.
-
Document test results and defects (If a test fails, you can manually create a defect in SAP Cloud ALM. You can then track, assign, prioritize, and follow the defect through to full resolution).
Cloud ALM helps ensure that every requirement is tested and validated before going live. It also provides transparency, so managers can easily monitor the quality and readiness of the solution.
Deploy phase
The Deploy phase is when changes are moved into the production environment. SAP Cloud ALM supports this process with structured deployment management tools.
With Cloud ALM, teams can:
-
Plan deployments using deployment plans and releases.
-
Document all software changes.
-
Ensure traceability & audit trails.
-
Track approvals and readiness.
-
Ensure that only tested and approved changes reach production.
This reduces the risk of errors during go-live and helps keep the system stable.
Here, SAP Cloud ALM allows you to track the full lifecycle of a feature. Once a feature is created, it moves to the In Specification status, where the customer can provide a detailed specification. From there, the feature progresses through development, testing, and deployment. When it’s ready, the Deployment Orchestration app helps connect the feature to transport systems, supporting both on-premise and cloud environments.
In the Deploy phase of SAP Cloud ALM, you can move features and changes to the target systems using integrated transport solutions. Cloud ALM connects to different transport tools depending on the landscape: The Change & Transport System (CTS) for S/4HANA Private Cloud, ABAP for on-premise, Adaptation Transport Organizer (ATO) for S/4HANA Public Cloud, Cloud Transport Management Service (TMS) for SAP BTP, Cloud Foundry, and other cloud environments. These integrations let project teams manage deployments directly from Cloud ALM.
SAP Cloud ALM for Operations
Once the system is implemented, ongoing stability and fault tolerance become essential. SAP ALM provides the tools to detect issues early, keep processes healthy, and ensure uninterrupted operations.
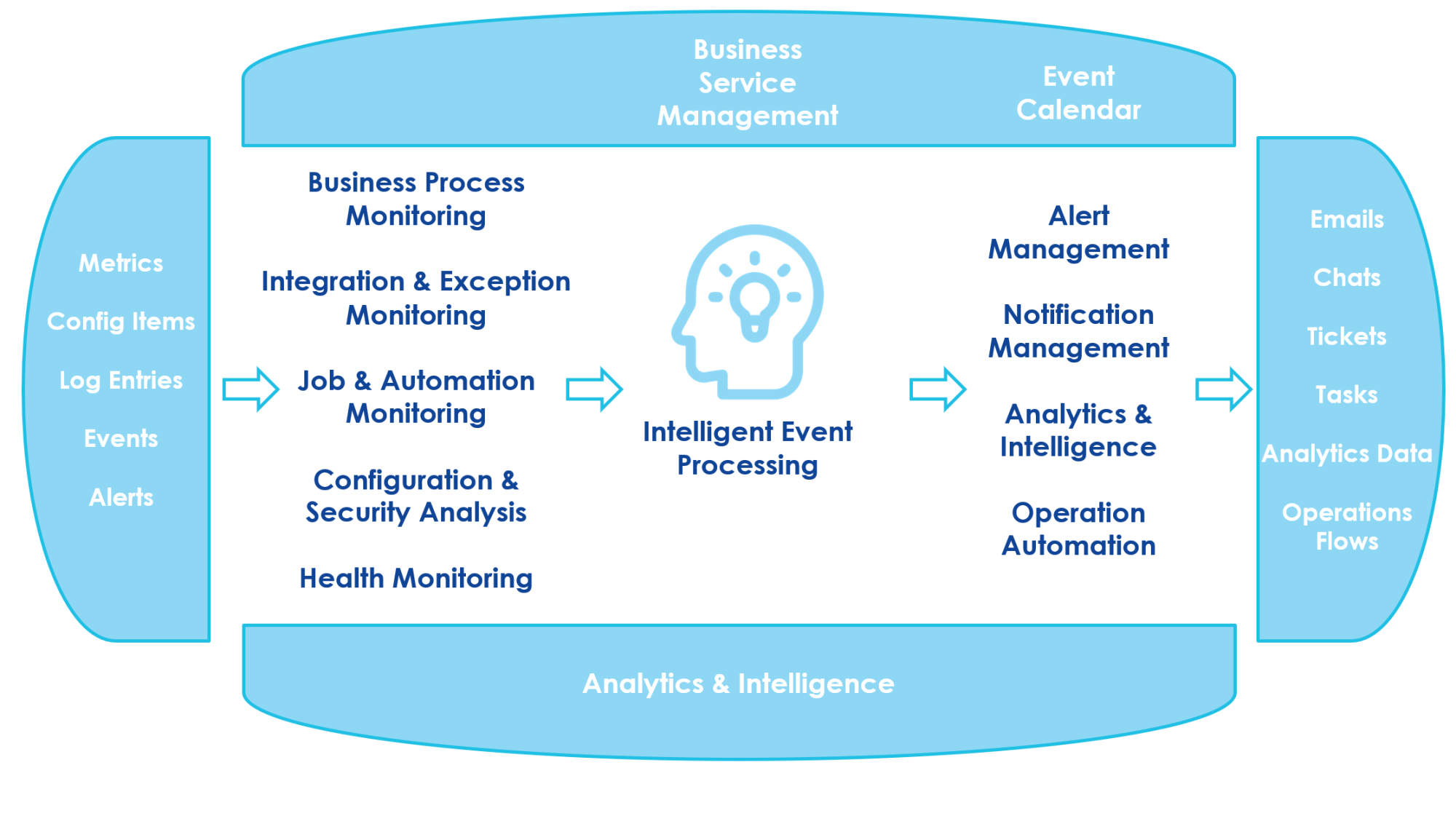
SAP ALM collects a wide range of technical and business signals that form the basis for all monitoring and analytics. These signals include log and event records, alerts, system metrics, background job data, user activity, and configuration and security data.
These raw inputs are fed into the Intelligent Event Processing engine. The engine evaluates the information, identifies anomalies, and transforms the findings into actionable insights.
SAP ALM provides several key monitoring areas that help maintain system reliability:
Business process monitoring: This feature monitors business processes end-to-end, compares actual performance against predefined or imported KPIs, evaluates overall process health, and detects unusual activity based on configurable thresholds. SAP Cloud ALM provides a large catalog of built-in KPIs that customers can use out of the box. Built-in KPIs help track process performance. Alerts are automatically raised when there are deviations. This ensures that issues are addressed before they impact business operations.
Integration and exception monitoring: It helps you see how data moves between your SAP systems. It works for cloud, on-premise, and hybrid landscapes and tracks both direct system-to-system connections and those using orchestration platforms. You can check the overall health of your integrations, get alerts when something goes wrong, and search messages using business attributes to find the cause of issues quickly.
User monitoring: It’s a way to check how well the system is working from the user's point of view. It combines real-user monitoring and synthetic monitoring. Synthetic monitoring uses Selenium IDE scripts that run regularly to measure UI response times. SAP Passport and related tools help measure how long it takes to complete important tasks. All this helps make sure that customers have good experience.
Job & automation monitoring: It gives you a clear view of all automated processes and background jobs across your SAP systems. You can see their current status, runtime, start delays, and any issues that occur. The tool highlights jobs that fail or behave unusually, lets you drill down into individual executions, and provides alerts if problems arise. You can also analyze historical trends to spot patterns and understand potential risks.
Configuration and security monitoring: This feature helps make sure your SAP systems are set up the right way and are safe. It regularly collects system configuration items and software versions into the Configuration and Change Database (CCDB), providing a centralized store of system settings. Users can browse the configuration store, search for patterns, and visualize content using the store browser. Cloud ALM lets you compare your current settings with recommended configurations, find differences, and use template configurations when needed. It also supports standardized analysis and reporting, which makes it easier to track changes, detect potential security issues, and generate actionable insights for system improvements.
Health monitoring: This one helps you keep track of the health of your SAP cloud services and systems. It collects technical metrics and events from both SAP SaaS applications and customer applications built on SAP BTP, as well as from SAP ABAP-based systems. The tool shows the status of important aspects like system connectivity, background jobs, and data persistence, making it easy to spot service disruptions or performance issues.
Business Service Management: It provides a single view of your business services and all the things that affect them. It shows the status and availability of each service, the connected cloud and technical systems, and any events that could impact performance or service level agreements (SLAs). You can also track all planned and unplanned events in a service calendar. This helps you understand how issues or maintenance activities influence overall service health.
Intelligent Event Processing: It puts all events and alerts from different systems into one place. It collects signals, connects related events, and sends them to the right place. You can set rules to react automatically or manage events manually when needed. The tool includes a central event log and an alert inbox for easy follow-up. It also links related events together. For example, it matches a manually created notification with an automatically generated alert. This gives a clearer picture of what is really happening.
After analysis, SAP ALM can automatically trigger outbound actions:
-
Email or chat notifications
-
Automatic ticket creation
-
Task creation for support teams
-
Direct links to analytics for deeper investigation
This creates a complete loop: detect an issue, understand its impact, notify the right people, and accelerate resolution. The outcome is consistent operational reliability and minimized downtime.
SAP Cloud ALM for Service
SAP Cloud ALM has a service area that helps customers work with SAP support and quality services. Its main goal is to give one clear place where SAP can deliver its service activities and where the customer can see all results and recommendations.
Here's how it works in real life. A customer asks SAP for a service, like a Technical Integration Check Session or Going live support session for a specific system. SAP performs the service, looks at the system through Cloud ALM, and then posts the results back to the customer’s tenant. The customer simply opens the Service section and sees everything: what SAP checked, what was found, and what SAP recommends doing next. This keeps direct communication with SAP simple and transparent.
SAP is also adding new capabilities that make service delivery convenient:
-
Service Delivery Center: A simple, unified interface where customers can access all service-related information. It shows past, current, and upcoming SAP services.
-
Service Results: A digital, structured format for service outcomes sharing. Customers can quickly drill down into details, explore findings and understand recommendations without searching through manual documents.
-
Issues & Actions Management: A clean and simple way to track all action items connected to SAP services. Customers can easily follow what needs to be fixed, what has already been handled, and what is still in progress.
At the same time, Cloud ALM does not include a full IT Service Management (ITSM) tool. There is no built-in service desk for handling internal or partner support tickets. Cloud ALM only creates automatic technical alerts when it detects problems, but these alerts are not the same as full support tickets.
For this reason, you can use one of the following options:
-
Connect Cloud ALM to an external ITSM tool.
-
Build a custom solution using Cloud ALM APIs.
Most customers still need a full ITSM system for their day-to-day questions, so an external service desk is usually required. Cloud ALM focuses mainly on service delivery from SAP, not on replacing a complete ITSM platform.
Benefits of SAP Cloud ALM
SAP Cloud ALM gives companies a faster, safer, and cheaper way to implement and operate their SAP landscape. Its tools cover the entire lifecycle, so teams can focus on real business value instead of manual work and endless coordination.
-
Faster go-live
Cloud ALM helps speed up implementation by offering ready-to-use configurations, guiding teams through an agile project flow, and reducing the need for custom code. Testing also becomes more efficient: you focus only on what matters, automate repetitive steps, and run tests much faster. -
Fewer disruptions
The platform constantly monitors your business processes, integrations, applications, and even user activity. It quickly highlights issues, helps teams resolve them faster, and can proactively detect problems before they cause downtime. Many corrective actions can even run automatically. -
Lower total cost of ownership
Cloud ALM is included in SAP cloud subscriptions and SAP Enterprise Support, so there’s no extra licensing cost. Projects become cheaper because activities are automated and accelerated, and operations cost less because routine tasks and fixes require fewer manual hours.
Conclusion
SAP's transition to a new generation of cloud products created the need for an ALM platform designed specifically for cloud landscapes. SAP Cloud ALM was introduced to support this shift. Although it is not positioned as a replacement for SolMan, it is a modern ALM solution built for a different class of systems: cloud and hybrid environments. Just as SolMan once supported on-premise systems, SAP Cloud ALM now provides the tools needed to run, monitor, and implement today’s cloud-based SAP solutions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the cost of SAP Cloud ALM?
SAP Cloud ALM usually doesn't require extra licensing costs. It's included in SAP Cloud Service subscriptions with Enterprise Support cloud editions, SAP Enterprise Support, and Product Support for Large Enterprises. Each customer gets one Cloud ALM tenant for every customer number as part of the subscription.
However, the included tenant has usage limits. By default, it provides 8 GB of SAP HANA storage and 8 GB of outbound API data transfer per month. This is enough for most customers.
But if you need more, you can purchase usage extensions. These extensions are sold in blocks and increase both storage and outbound data transfer by 8 GB each. If you have more Cloud ALM tenants than the one included in the subscription, you will have to pay extra. Third-party tools integrated with Cloud ALM, such as Tricentis for test automation, are licensed separately.
This SAP note describes methods for monitoring usage metrics.
The SAP guide provides information about using multiple SAP Cloud ALM tenants.
Does SAP Cloud ALM include service desk capabilities?
SAP Cloud ALM does not include IT Service Management (ITSM) or a service desk. It's not meant to replace internal incident or ticket management tools. Instead, it integrates with external, third-party ticketing systems via APIs. Some tools, such as Jira and ServiceNow, can be connected using ready-made connectors.
SAP Cloud ALM for Service focuses specifically on SAP-delivered services. It displays service results, recommendations, and action items provided by SAP. However, it does not function as a general service desk for handling internal company incidents or partner support tickets.
Is SAP Cloud ALM replacing SAP Solution Manager?
Both SAP Cloud ALM and SAP Solution Manager serve application lifecycle management needs, but they are designed for different types of landscapes. SAP Cloud ALM focuses on cloud and hybrid environments, whereas SAP Solution Manager was primarily built for on-premise SAP systems.
As SAP continues to expand its cloud portfolio, the company recommends transitioning to SAP Cloud ALM for landscapes that include SAP cloud solutions since Cloud ALM fully supports their implementation and operation. When planning such a transition, customers should evaluate whether SAP Cloud ALM can support all the functions required by any remaining on-premise systems in their landscape.
Which SAP systems are supported by SAP Cloud ALM?
SAP Cloud ALM is designed primarily for cloud and hybrid SAP environments. An up-to-date list of supported systems is available here
Is SAP Cloud ALM suitable for on-premise SAP landscapes?
SAP Cloud ALM partially supports on-premise SAP landscapes, particularly smaller or less complex ones. However, it does not offer the same full functionality as SAP Solution Manager. Key capabilities commonly used in on-premise environments, such as Change Request Management and Data Volume Management, are not available in Cloud ALM.
Cloud ALM also takes an agentless approach, connecting to systems via REST APIs instead of traditional RFC-based integrations. Due to these differences, Cloud ALM performs best in cloud-first or hybrid landscapes. For complex, on-premise heavy environments, SAP Solution Manager may still be required.
